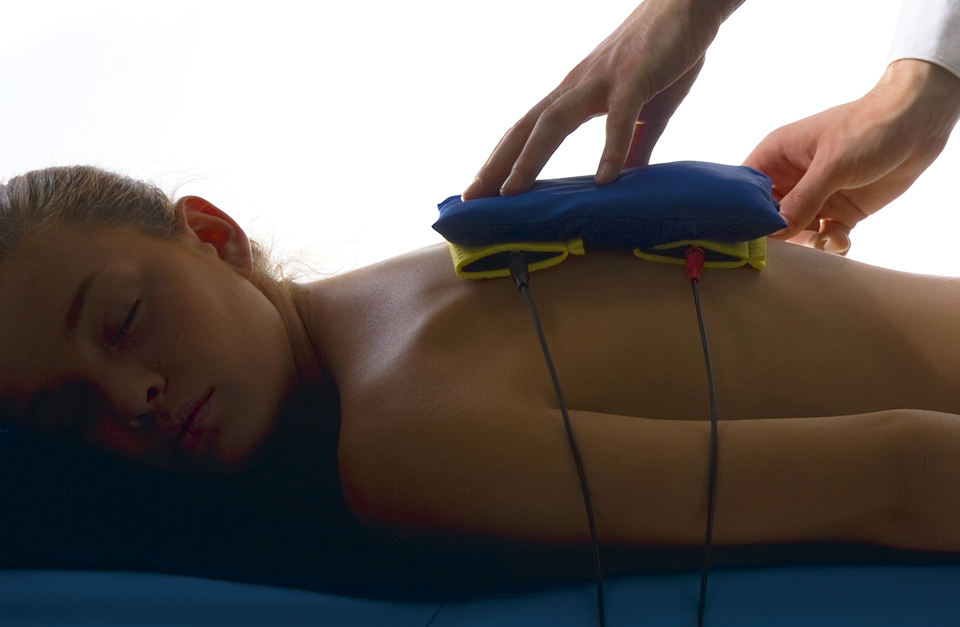
What is electrotherapy?
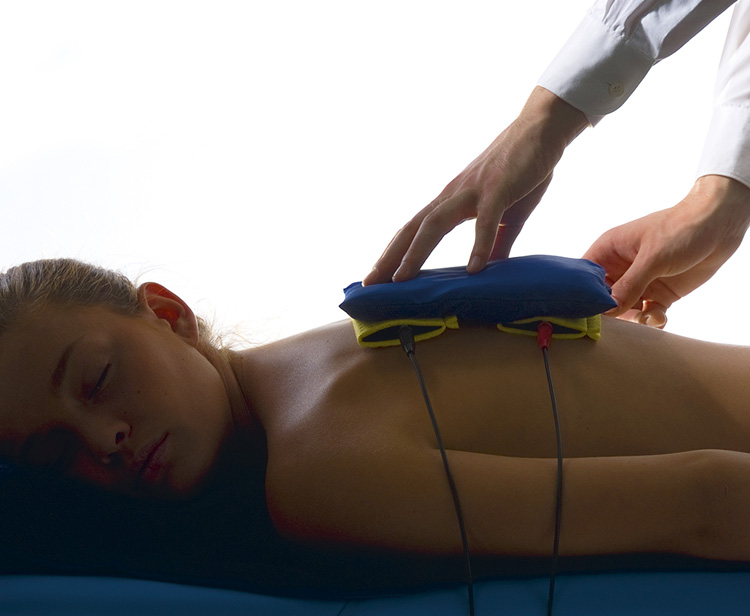
Electrotherapy is a field of physical therapy involving the treatment of diseases of the neuromuscular system using currents with various waveforms, frequencies and intensities, as well as modulated in both amplitude and frequencies. It is used both in medicine and rehabilitation of patients, as well as complementing other forms of physical therapy. The aim of the treatments is to treat pain, increase tissue blood flow and stimulate them to accelerate regeneration. Electrotherapy also supports the absorption of swelling and exudates in the joints resulting from injuries and overloads. The range of possibilities offered by electrotherapy allows to achieve a wide range of therapeutic effects.
There are several current waveforms that show beneficial effects on tissues: TENS pulse currents, SP-TENS pulse currents, interferential current (according to Nemec), galvanization, ionophoresis, microcurrents, EMS current, tonolysis, Trabert current, diadynamic current (developed by Pierre Bernard), Kotz current (Russian Stimulation), triangular and rectangular pulse currents and unipolar sine surge current. Their use is selected based on the patient’s needs and his/her individual sensitivity to stimuli. Individual methods differ from each other depending on the shape of the pulse, its duration, amplitude, variable or constant frequency and its value. The number of electrodes, their size and the way the current flows are also selected for the treatments used, depending on their location. Electrotherapy is particularly valued because of the safety and effectiveness in the treatment of pain.
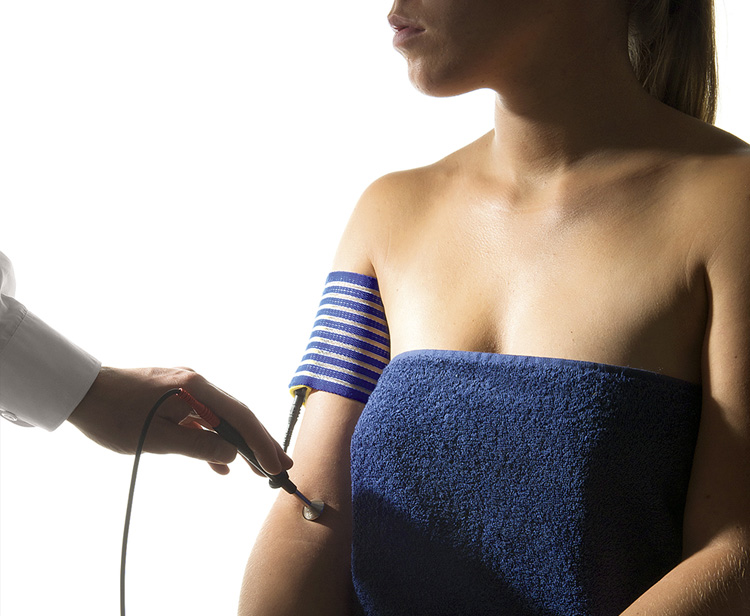
How does electrotherapy help patients?
The electric current used in physical therapy has an impact on the electrophysiological processes occurring in the body’s cells. The most desirable healing effects are: stimulation of nerves and muscles, acceleration of tissue regeneration, muscle relaxation, pain relief, treatment of inflammation and tissue regeneration. For this reason, it is used both in sports injuries and wounds, as well as in the treatment of diseases of the neuromuscular system (degenerative ailments, neuralgia, arthrosis or inflammation of the nerve plexuses).
Electrotherapy is also an inseparable element of rehabilitation of patients with physical disabilities.
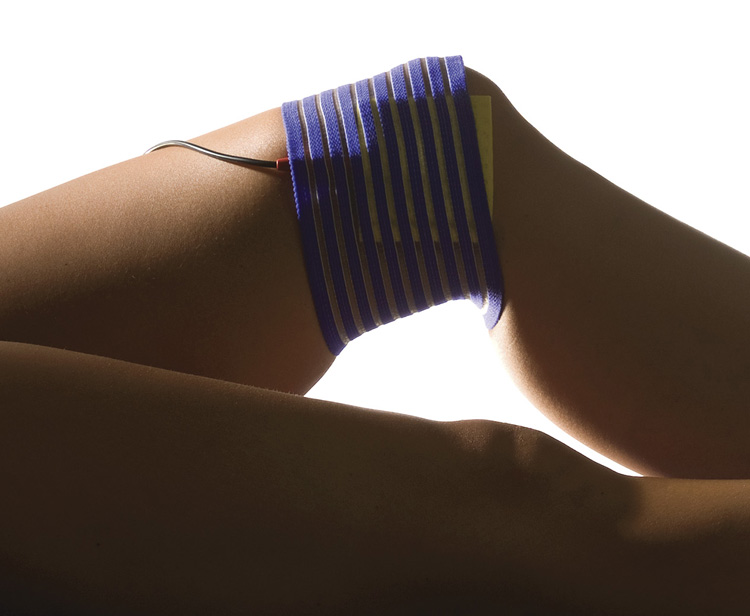
The use of electrotherapy.
What diseases does electrotherapy treat?
The multitude of applications of electrotherapy and its beneficial effect on the body allows achieving positive therapeutic effects in many diseases and ailments. Electrotherapeutic treatments, by widening blood vessels and improving blood circulation, improve tissue nutrition and regeneration capacity. They increase the comfort of patients suffering from chronic diseases and support the rehabilitation of those with musculoskeletal system diseases.
Electrotherapy has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, among others, thanks to endorphins releasing, trophic and tonic actions and by activating the Melzack’s and Wall’s “gate control”.
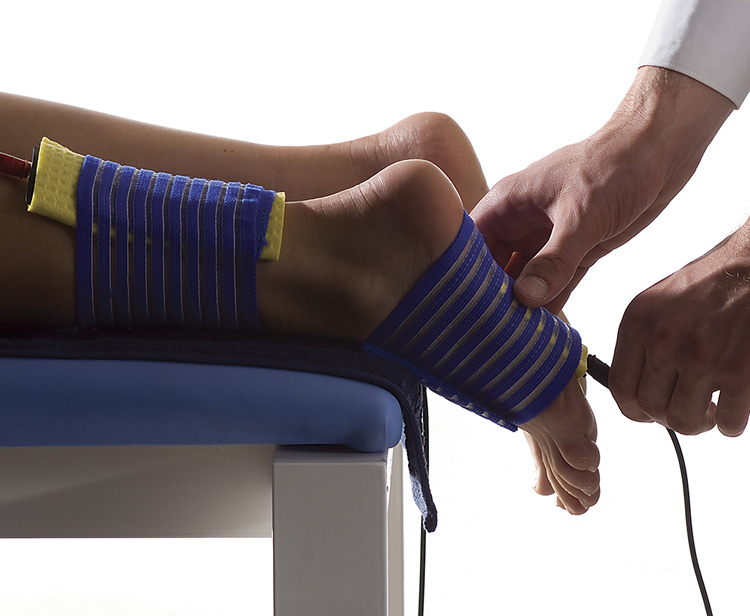
Electrotherapy supports the healing and rehabilitation processes in the following conditions:
- Pain syndromes and inflammatory conditions – joint pain and pain syndromes in the course of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS), spinal pain due to osteoarthritis, neuralgia and compression syndromes, periarticular inflammations, root syndromes (e.g., sciatica), discopathies, acute and chronic pain of known etiology.
- Post-traumatic conditions and injuries – musculoskeletal injuries, soft tissue injuries around joints, edema, subcutaneous and intramuscular hemorrhages, hematomas.
- Tissue regeneration and wound management – chronic wounds, pressure ulcers, and skin ulcers.
- Muscle tone disorders and atrophy – conditions with increased muscle tone, muscle atrophy due to immobilization, reduction of spastic muscle tone.
- Neurological and nerve disorders – partial damage to afferent nerve fibers, electrostimulation of nerves, electrostimulation of properly innervated skeletal muscles, electrostimulation of denervated skeletal muscles, electrodiagnosis including I/t curve assessment.
- Circulatory and autonomic disorders – vascular syndromes, peripheral circulatory disorders, thrombosis prevention after surgical procedures, reduction of symptoms associated with gynoid-type lipodystrophy.
This website uses technical and functional cookies or internet analytical cookies, with your consent marketing cookies. You can read more about this in the Cookies Policy and the Information Clause. By accessing the website, you agree to them according to your browser settings. You can change them at any time, and if you do not do so, browsing the website will use these files.